Claire (Y11) investigates the relationship between Twilight and two classic novels, Jane Eyre and Wuthering Heights, to discover what makes them similar but more importantly what divides them.
It is a truth universally acknowledged that books written about vampires are almost exclusively terrible, and in no case is this truer than in that of Twilight. Widely considered to be one of the worst books ever written, it is generally believed to have absolutely no literary merit whatsoever, despite the story itself being age-old and popular under many other circumstances. Among those circumstances is Charlotte Brontë’s Jane Eyre, and to a lesser extent, Emily Brontë’s Wuthering Heights. What is interesting is that both of those books are hailed as literary classics and taught on many school curriculums, despite the fact that in terms of storyline, there is very little that actually separates them from Twilight. So why is it that the Brontë sisters’ novels are deemed masterful works of literature, whilst Twilight is relegated to the trash pile?
In many ways, the books are very similar. All three have a brooding, Byronic male protagonist – Edward Cullen, Edward Rochester, and Heathcliff – who falls in love with a female protagonist – Bella Swan, Jane Eyre, and Catherine Earnshaw. There are definitely some differences in the traits of these female protagonists, but at a basic level, they are addicted to their counterparts in a ‘passionate’ love which actually seems more like an abusive relationship. Catherine says, “I am Heathcliff”, a sentiment very similar to Bella’s expression that “(her) life was about (Edward)” and although Jane famously states that she is a “free human being with an independent will”, apparently marking her out as not being as addictively in love as Catherine and Bella, she does eventually fall prey to the same obsession.
All three stories are also set in isolated locations, cut off from society and rendering the romance central to the plot as there is very little outside influence. Bella finds herself in the small American town of Forks, where Edward and his family take centre stage as local curiosities. Jane is relegated to Ferndean Manor, which itself is located deep within the forest, and the other characters have little influence on her relationship with Mr Rochester. And Wuthering Heights, of course, is set in the iconic Yorkshire moors, where the surroundings seem to reflect the dynamic of the relationship – harsh, inhospitable, and inexplicably alluring. This feeling of isolation, this detachment from the outside world is what allows all three romances to blossom into the obsessive and damaging relationships they ultimately become.
There are other similarities, of course. All three female protagonists are ‘othered’ by society, be it by virtue of simply being a teenage girl or by their feminist principles. All three are ceaselessly self-obsessed; Jane dwells on herself endlessly, Bella is conscious of her every flaw, and although Catherine seems far less self-deprecating, that does not mean she is not selfish. And throughout all three novels runs a feeling of the scandalous, the inappropriate and the exciting. Edward is, of course, a vampire, and over 100 years older than Bella is. Mr Rochester is Jane’s employer, and there is a gap in class and age. Heathcliff is Catherine’s adopted brother, and implied to be Romani in origin – certainly, he is not white. These factors tie common threads between the stories, linking their characters.

 What is it that renders Jane Eyre and Wuthering Heights simply better novels than Twilight?
What is it that renders Jane Eyre and Wuthering Heights simply better novels than Twilight?
So if the characters are essentially the same, the setting is essentially the same, and the basic storyline is essentially the same, what is it that renders Jane Eyre and Wuthering Heights simply better novels than Twilight? One of the most obvious factors is the context. The Brontës were women writing books at a time when women generally didn’t, and although their novels were published under pseudonyms, it does not detract from the fact that they rebelled against the norm and published works of fiction which went on to become classics. It would have taken extraordinary courage and talent to write and then attempt to publish such literature, and it shows in the novels themselves. By contrast, Meyer was able to sit down and simply write, and then have her book published with relative ease. This means Twilight, although not altogether terrible, is simply very boring. It is not a novel of challenge and struggle, and that too shows in the writing.
Another thing that marks the Brontë sisters’ works from Meyer’s is the fact that Wuthering Heights and Jane Eyre are, objectively, better-written. The prose style of Twilight is simple, bland and unremarkable – the descriptions are extremely mundane and Bella’s simpering first-person style is insipid at best and exasperating at worst. In contrast, both Brontë sisters offer rich and interesting writing, replete with elegant descriptions of landscape and emotion, and when Jane narrates, her first-person voice is, although occasionally irritating, undoubtedly compelling. Wuthering Heights is also a much more complex story, spanning generations of characters without losing track of the development of any, and although it is not the polished masterpiece that Jane Eyre is, it is certainly a triumph. Twilight is, to put it kindly, not.
None of this is to say that Twilight isn’t worth reading. All literature has an inherent anthropological value, in that it teaches us about the culture of the time, and Twilight does a very good job of informing readers that in the mid-2000s, people were obsessed by vampires. The undeniable fact, however, is that it is not a particularly good book, and that for all its similarities to the Brontë sisters’ masterpieces, it does not hold up well in comparison.
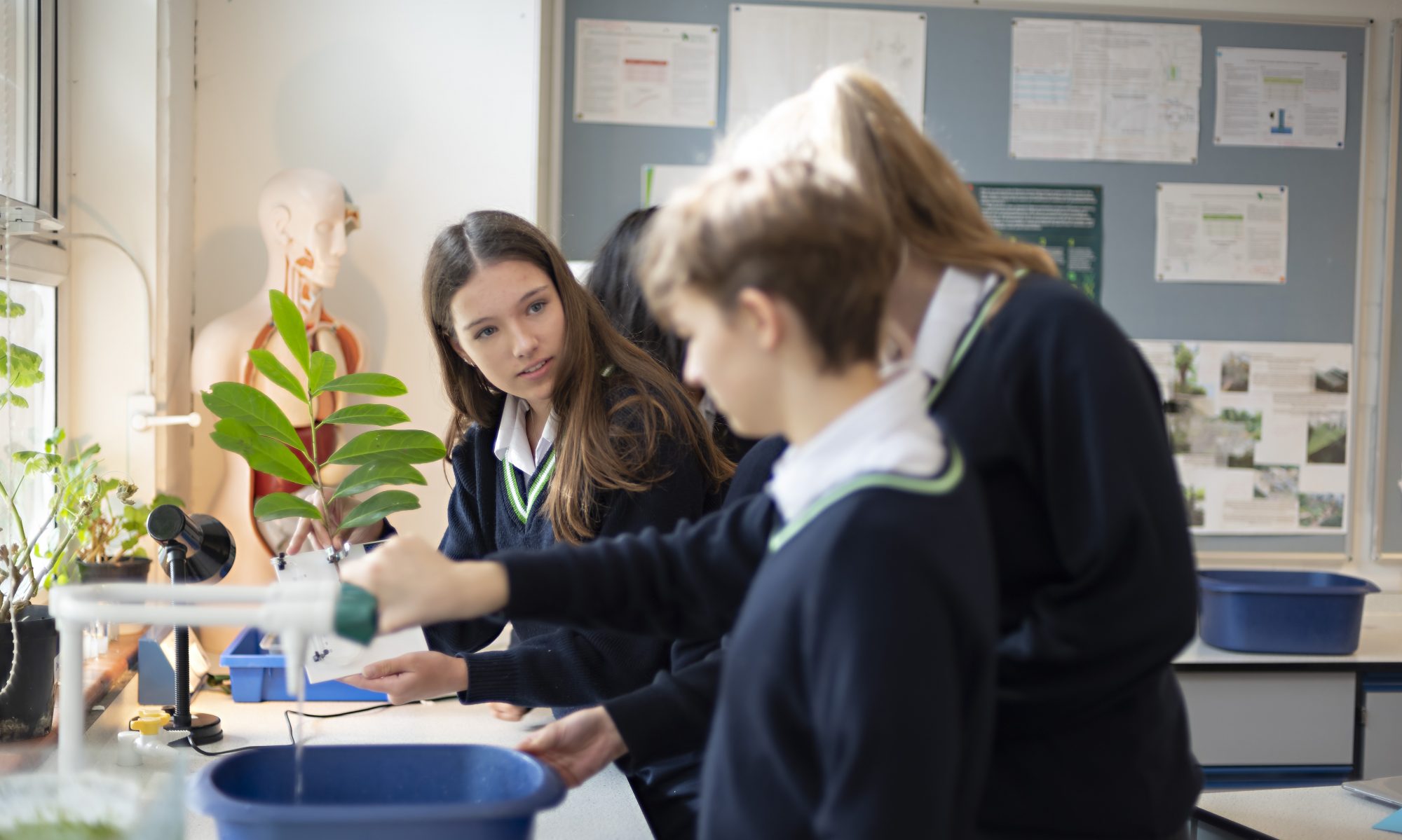



 We prefer ‘Stepping In’…… I fondly call my new cohort of Year 7s on their first day (or should I say term?), ‘turtles’…. their backpack has their life in it and appears to dwarf them as they wide-eyed, set off down school corridors navigating their way around what will be ‘home’ for the next 7 years.
We prefer ‘Stepping In’…… I fondly call my new cohort of Year 7s on their first day (or should I say term?), ‘turtles’…. their backpack has their life in it and appears to dwarf them as they wide-eyed, set off down school corridors navigating their way around what will be ‘home’ for the next 7 years. The crux of her book ‘Daring Greatly’
The crux of her book ‘Daring Greatly’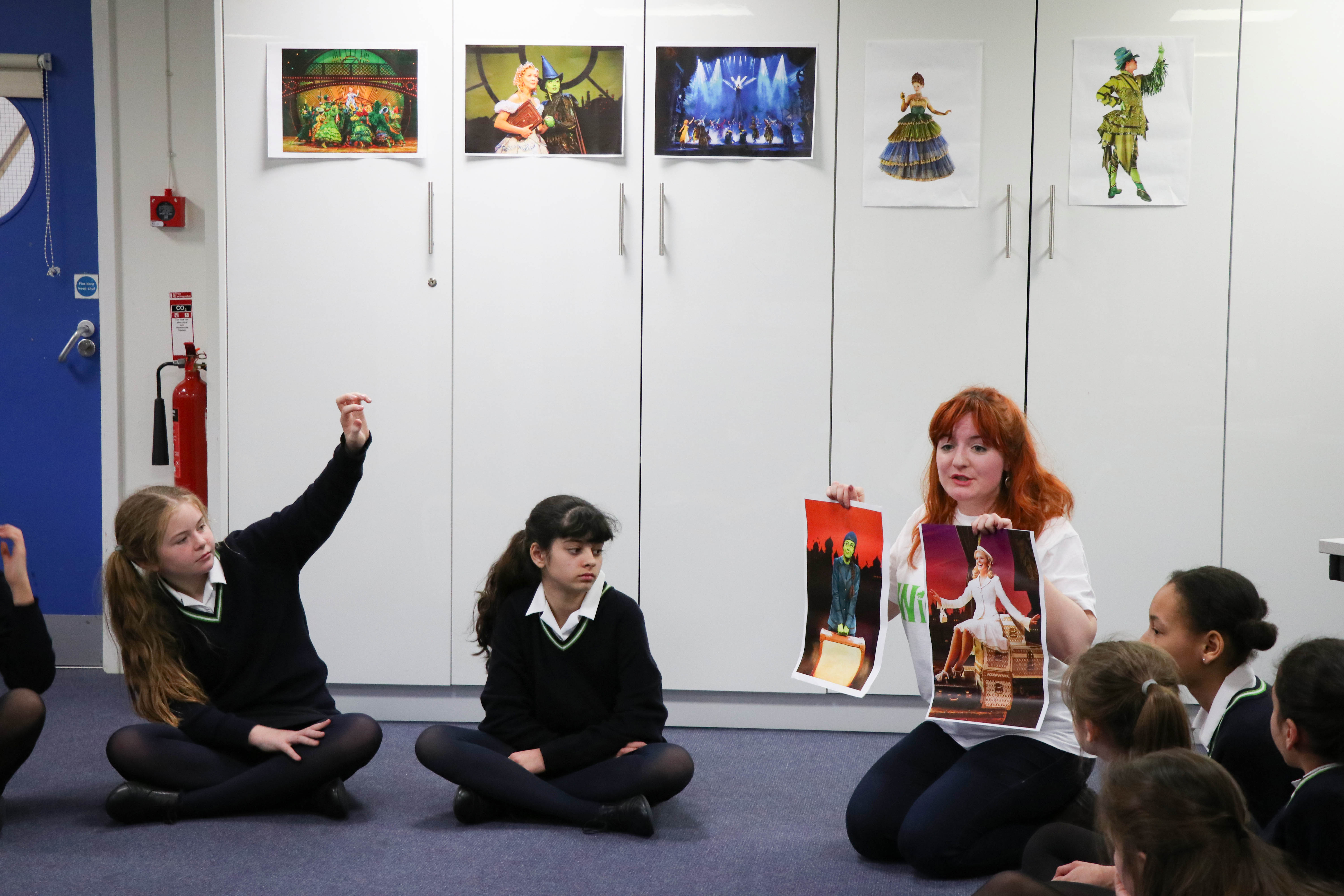









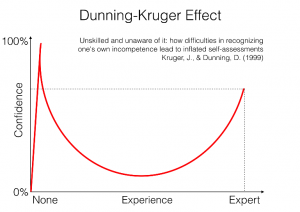 They say a little knowledge is a dangerous thing. If we consider the Dunning-Kruger effect (demonstrated on the diagram to the right) we might agree. The principle is that ‘knowledge without sufficient experience can lead to an overestimation of ability’. It is no surprise that Donald Trump has been nicknamed the ‘Dunning-Kruger President’ in articles by the New York Times, Bloomberg, and the Independent. I recall an interview where he tries to explain uranium to his audience:
They say a little knowledge is a dangerous thing. If we consider the Dunning-Kruger effect (demonstrated on the diagram to the right) we might agree. The principle is that ‘knowledge without sufficient experience can lead to an overestimation of ability’. It is no surprise that Donald Trump has been nicknamed the ‘Dunning-Kruger President’ in articles by the New York Times, Bloomberg, and the Independent. I recall an interview where he tries to explain uranium to his audience:


