Jenny Cox, Director of Co-curricular and Partnerships at Wimbledon High, looks at the links between co-curricular activities and the impact these can have on academic outcomes in the classroom.
There has been much research over the years investigating the link between Sport and its benefits – not only to a healthy lifestyle – but to the academic progress of students in schools and universities. Research has shown that regular physical activity leads to improvements in a range of cognitive functions, including information processing, attention and executive function (Chaddock et al. 2011). However, does involvement in any co-curricular club facilitate academic outcomes?
‘Flow’
Can you think of a time when you have ever been so absorbed in an activity that you have completely lost track of time? That whatever you were doing was challenging, totally captivating, was extending your skills and you were virtually operating in the subconscious? If you can, it’s likely that you were experiencing a phenomenon known as ‘flow’. Psychologist Csikszentmihalyi writing in the 1960s researched this initially with it really coming to the forefront of sports psychology in the 1990s.
He described it as:
“A deeply rewarding and optimal experience characterised
by intense focus on a specific activity
to the point of becoming totally absorbed in it”
Csikszentmihalyi suggested that experiencing ‘flow’ makes us happier and more successful, which in turn leads to increased performance. To get to this point, he pointed out that tasks have to be constantly challenging which in turn results in personal growth and development. This doesn’t mean that we always have to be in a state of optimal performance, but more that we are fully immersed in the process of the task in hand, as shown in the diagram below:
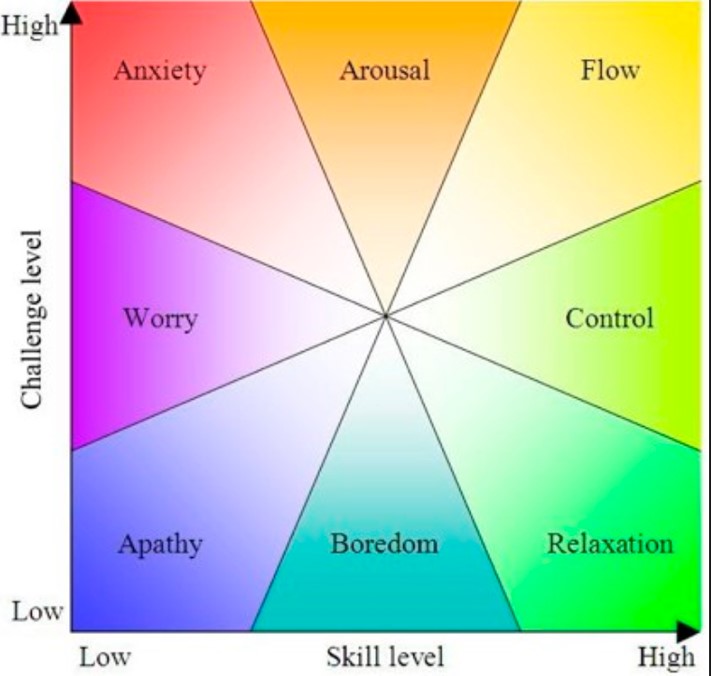
‘Flow’ experiences can happen as part of everyday life, and Csikszentmihalyi suggested overlearning a concept or a skill can help people experience flow. Within a sporting context, it is sometimes referred to a “being in the zone”, experiencing a loss of self-consciousness and feeling a sense of complete mastery.
Motivation
In addition to overlearning, another key component of finding ‘flow’ is doing activities that we are intrinsically motivated to take part in. This means work and activities that we feel real meaning behind and enjoy doing for the sake of doing. Financial gain, awards and praise can be by-products of the ‘flow’ activities you do, but they cannot be the core motivation behind what you’re doing. Csikszentmihalyi even goes further, saying the feeling should be “such that often the end goal is just an excuse for the process.”
Academic success
So why is this relevant to our school co-curricular programme and can it be linked to academic success? The links here are two-fold.
Firstly, the co-curricular programme is designed to inspire and enhance the general learning of new skills and concepts. It gives us more time to focus on over-learning a skill or concept because there is no pressure of being examined, therefore no exact specification or course content to get through. We have the luxury of taking our time, over-rehearsing, over practising to a point of taking part in an activity with a loss of sub-consciousness. We may repeat skills so frequently because we revisit them two, three, four, seven, eight times a week, (think of rowing, drama, and music to name just three activities that have repeat weekly sessions), that the feeling of knowing a skill, a sequence, a technique really well and performing is sub-consciously really does happen.
Secondly, with this feeling of ‘flow’ comes those ‘magic moments’ we can all benefit from at any point during the day. The mere fact we are immersed in activity we enjoy could result in us being ‘in the zone’. We are busy immersed in something which is likely to mean we are automatically not thinking about an essay, a grade, a piece of coursework, a friendship or relationship issue at that time and so as a consequence that time contributes enormously to our state of well-being and happiness. This, in turn, is highly likely to lead to a more productive ‘head space’ for work when we return to it, less procrastinating, greater focus and possibly better outcomes.
So can we draw a link between participation in co-curricular activities and academic outcomes? There is research to indicate we can….. happy reading!
–
References
-
Chaddock, L., C. H. Hillman, S. M. Buck, and N. J. Cohen. 2011. “Aerobic Fitness and Executive Control of Relational Memory in Preadolescent Children.” Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 43 (2): 344–349.
-
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience. Harper & Row
-
Bailey R. (2016): Sport, physical activity and educational achievement – towards an explanatory model, Sport in Society
