Things that you can search on Google, Youtube, Tiktok, Instagram, whatever, only make up about 5% of the internet.
‘What’s the other 95%?’ you may ask.
Well, that’s a tough question to answer, because some of it you can’t access with a normal search engine on your phone or computer.
To understand why this is the case, we need to know a little bit more about the internet.
How the Internet ACTUALLY Works (in extremely simple terms)
Contrary to popular belief, the internet is NOT a cloud. It’s actually better modeled as a wire. Think of it like this: If you had a wire and you hooked a computer to each end of it, the two computers could communicate with each other through that wire.
Congratulations, you have an internet!
Unfortunately, this internet sucks compared to the ones that we use every day. This is because the two computers can only share the information that they have. And with only two computers, you’d get bored pretty fast. Luckily, the actual internet is connected to a LOT of computers. And these computers are connected to even more computers across the globe. So to keep track of all of these computers, each piece of the network has an address that looks like this:
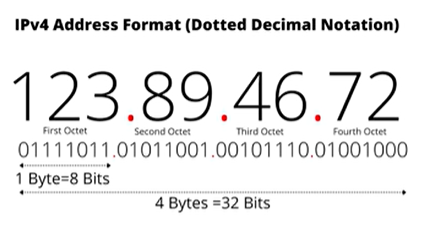
These numbers are pretty hard to remember, so they get turned into links! (like this):

Each file that you send and receive has a known origin point and destination point. It finds its way to and from these points by going through a network and telling each computer where it needs to end up, so that computer can send it onto the right path.
So let’s say you want to search up your bank’s website on Google, so you can log into your account. Your computer will send your search for HSBC to Google, and it gives you a long list of results that you can choose from:
Congrats, you just interacted with the surface web, A.K.A. the first 5% of the internet!
But what’s the use of searching up your bank website if you can’t access your account?
Well, the reason why you can’t Google your bank account’s login is because if you could Google it, everyone else would be able to Google it too, and you’dprobably lose a lot of money.
Your bank account isn’t available on a search engine like Google because it’s not listed on the surface web. Instead, it’s a part of the ‘deep web’, which makes up the next 90% of the internet.
The deep web- anything that is password protected, under a pay wall, etc. (like your bank account)
BUT WAIT! We’re still not up to a hundred percent!
Yes, you guessed it, after the deep web comes the DARK WEB, making up the last 5% of the internet.
Why Does the Dark Web Exist, and How Does it Work Differently from the Internet?
First of all, when you use the normal internet, you’re being tracked by companies, who get permission to track you through the government. That’s why when you like a post of an influencer’s brand partnership with JD sports on Instagram, suddenly JD sports advertisements and other fitness-related content start flooding your Spotify, interrupting your YouTube videos, and infiltrating your ‘for you page’–you have been TRACKED and IDENTIFIED as someone who might be into sportswear.
But not everyone likes the idea of being tracked by the government, probably you included. And the crazy thing is, this means you and the government have a lot in common, because they don’t like being tracked by other governments, either. For example, the U.S. probably doesn’t want to be spied on by Russia.
This is why in the 1990s, researchers at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory developed something called ‘onion routing’, a form of data encryption that made it very hard for Russian hackers to intercept and open U.S. government files while they were being transported from computer to computer.
Unlike the regular internet, onion routing protects any data transmitted through it by wrapping it in multiple layers of encryption.
Encryption in simple terms- basically jumbling up the data in a file so that only the sender and receiver have the code to decrypt it.
In onion routing, an encryption process happens multiple times, so the file ends up being a secret code wrapped in a secret code wrapped in a secret code…and so on (hence the term ‘onion’).
If the White House wants to send a highly classified government document to Downing Street, they will put it in an onion file. On its journey, the onion file has topass through a bunch of checkpoints in order to be fully decoded, and only the file knows the path it has to take to its final destination. What’s more, each checkpoint on that path only knows how to decode one layer of the ‘onion’. After travelling through each layer, the file is finally decrypted and can be viewed normally.
So, while the onion file is going from D.C. to London, Ivan the Russian hacker (Ivan is not real, he is just for the sake of the example) can’t hack it, because he doesn’t know how to decode each layer of encryption in the right order.
This innovation was monumental for the U.S. government, as it enabled them to send files anonymously, without anyone knowing it was them.
Right?
Actually, no. You would immediately know it was them, because at the time, they were the only ones using the onion file software. This meant if Ivan were to find an onion file travelling through a network, he would be like, ‘this is obviously from the U.S. government and I am going to steal it!’
Even though Ivan wouldn’t necessarily be able to decrypt all the layers of the onion file and see what it is, he WOULD be able to intercept it and prevent it from reaching its final destination.
This was bad for the U.S. government.
The Creation of the Dark Web
The only way the U.S. government could remain anonymous was to open the onion routing service to the public. This meant that onion files could come from ANYWHERE and ANYONE.
What could possibly go wrong?
Well, if it wasn’t already crystal clear, giving everyone access to a global network where they could stay completely anonymous wouldn’t just attract the nerdy computer kids.
Turns out, it did attract the nerdy computer kids. AND the nerdy computer kids who were also really weird. To keep things year 7 appropriate, that’s all I’m going to say on that.
Moving on, this onion routing service is called the Tor browser (which is completely free and legal!).
DISCLAIMER: PLEASE do NOT try to access this site, as you risk a bunch of viruses being downloaded onto your device and stealing your information!!!
At this point you might be asking yourself, how would someone even buy something on the dark web, if they’re completely anonymous and therefore cannot use their bank card since it’s tied to their name?
If you weren’t asking that, I am going to tell you anyway.
If you were asking that, you’re right! If you used your credit card to buy something on the dark web, the NCA (National Crime Agency) would probably be at your door within minutes. So instead, the dark web uses Bitcoin.
Yes, while all of the finance bros are holding their bitcoin until the end of time, THERE’S ACTUALLY PEOPLE OUT THERE WHO USE IT!
Now, while it’s been a wild ride exploring the secrets of the immensely illusive and mystical dark web, I must stop here for my own safety, as well as yours. This brings me to the actual academic reason for me writing this piece:
What are the Economic/Moral Implications of the Dark Web and its Creation?
#1: The Growth of the Black Economy
One of the biggest economic implications of the dark web is its contribution to the black economy. The black economy (also sometimes called the hidden economy, the black market, the informal sector, and many other things) is basically made up of any economic activity that goes undetected and is not kept in the government’s official records.
One myth is that the black economy is drugs, weapons, and illegal substances galore. While all of these things can be and are traded within the black economy, a transaction as innocent as selling a neighbour your old kettle because they asked if you had one, them paying you in cash, and you bringing the kettle over to their house the next day is considered undetected economic activity, which is also part of the black economy.
Getting back to the point, because the dark web allows users to trade anonymously using cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, almost all transactions go untaxed and unregulated. This can reduce government revenue and make it harder to measure the real size of a country’s economy (known as GDP). For example, when people buy illegal goods or services online, those transactions don’t appear in official statistics, meaning governments can underestimate how much economic activity is actually happening (and they can’t tax it!). In simple terms, the dark web hides a portion of the world’s wealth and trade from view.
#2: Information Asymmetry
The dark web also creates a massive problem of information asymmetry, which is a situation where one party in a transaction knows much more than the other, meaning they might be able to exploit them.
On the surface web, platforms like eBay or Amazon rely on reviews, customer protection, and brand reputation to make buyers feel safe. On the dark web, those systems don’t exist, because everyone is anonymous. Sellers could lie about what they’re selling, or disappear entirely after being paid.
This uncertainty makes dark-web markets extremely risky and inefficient compared to regular markets, and shows how transparency and regulation are essential to protect consumers.
#3: The Right to be Anonymous
While it’s easy to focus on the dangers of the dark web, its very existence raises an important moral and economic question: should anonymity online be a right that everyone has?
From an economic perspective, online anonymity can empower individuals in countries with strict censorship, allowing them to share information, express opinions, and trade freely without government interference. In that sense, it supports the freedom of information, which is crucial to maintaining global economic progress. However, complete anonymity also removes accountability, which allows illegal markets and harmful activities to flourish.
The challenge, then, is finding a balance where people’s right to privacy is protected, but that privacy is prevented from becoming a means of exploitation.
At the end of the day, the dark web is a strange case study that proves even things which were once created to protect people can have some seriously unpredictable side effects.
